Data Mapping: Adding Systems Manually
Introduction
In this tutorial, you'll add a new system manually to your data map. By the end of this tutorial, you'll understand systems and data maps, and how to manage them in Fides.
Prerequisites
For this tutorial you will need:
- A Fides Cloud or Fides Enterprise account
- The role of
OwnerorContributorfor your Fides organization.
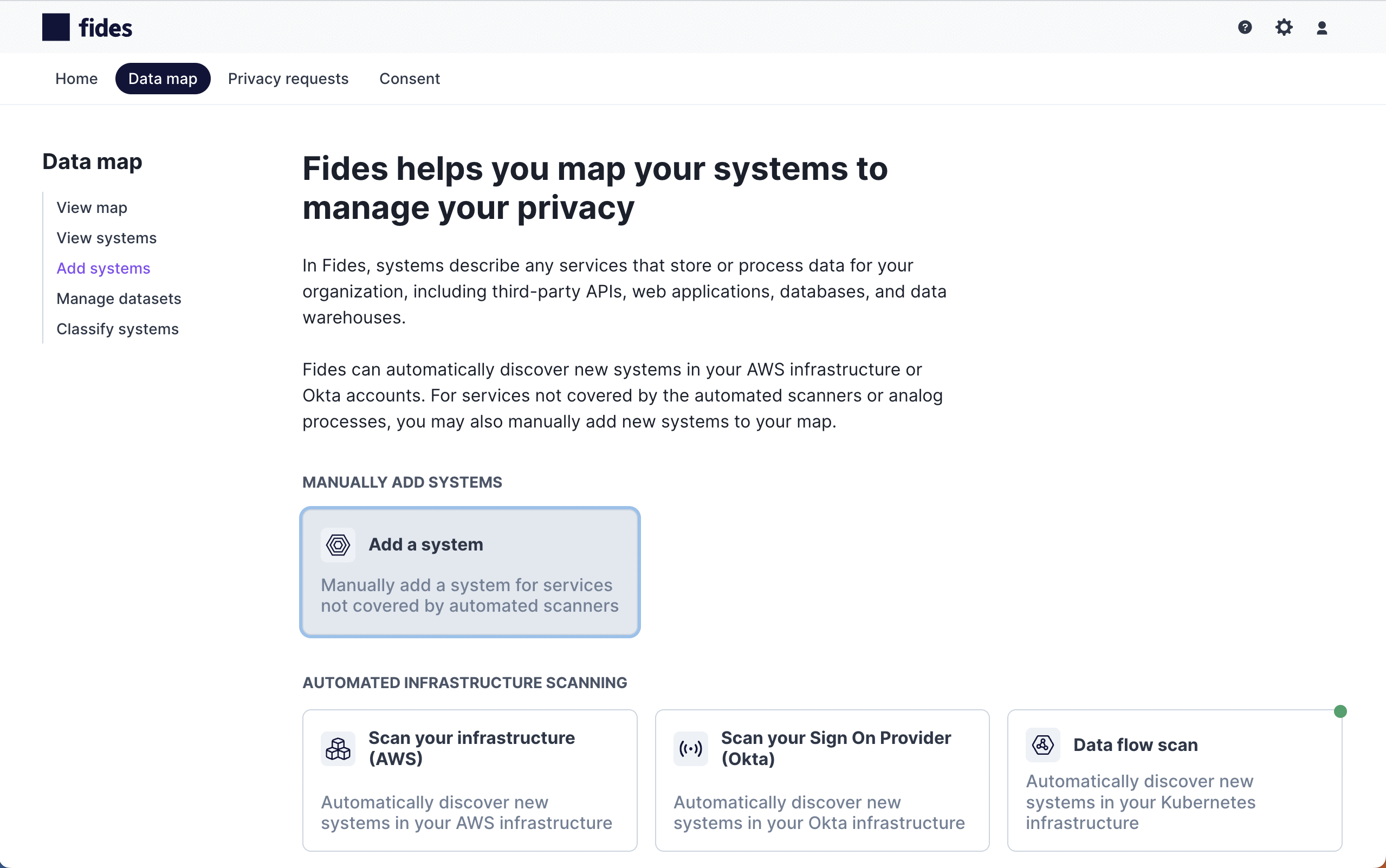
Adding systems manually
To start, navigate to Data map → Add systems and choose Add a system to add a system manually.
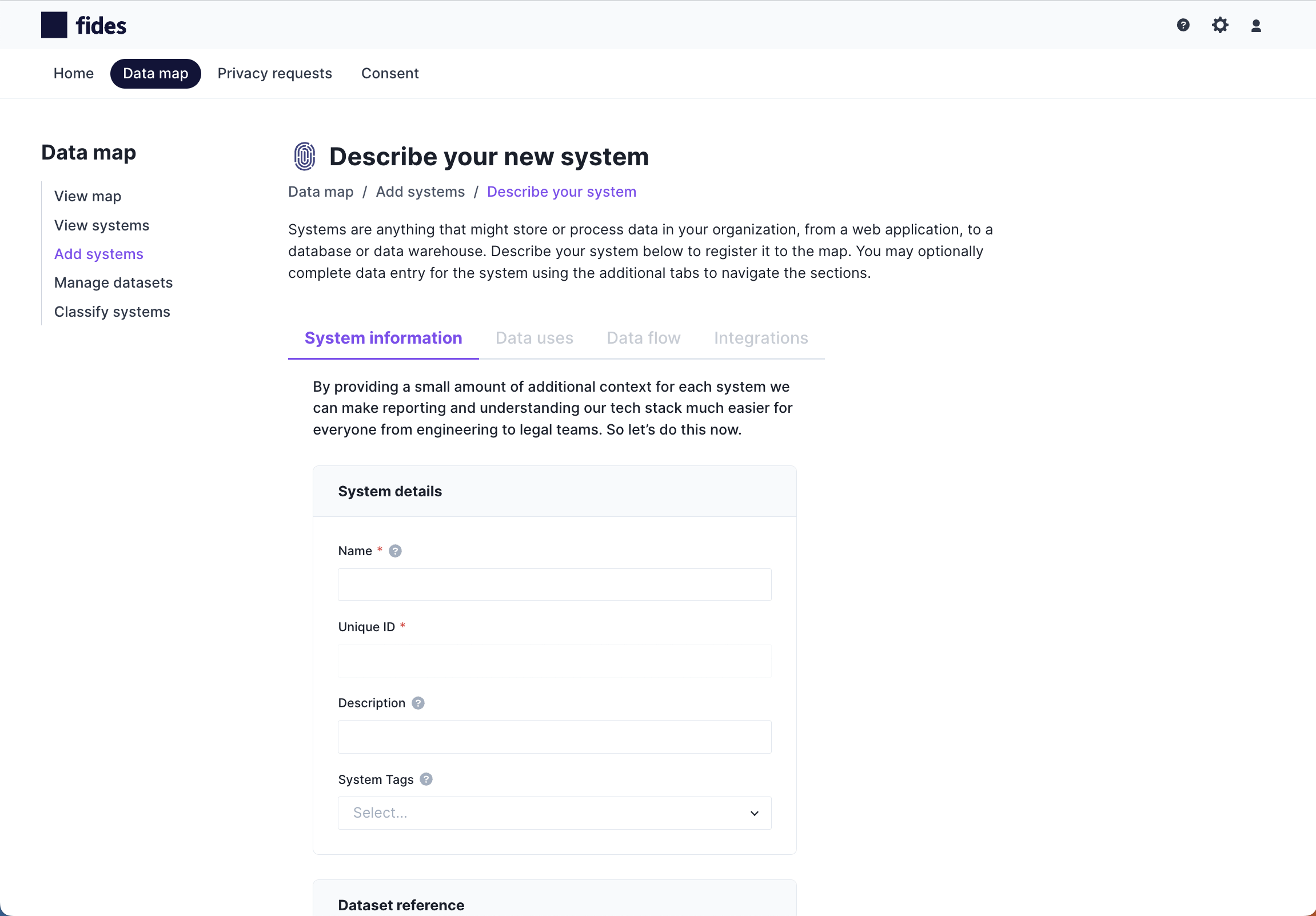
Complete your system's information
Create your system by completing the required System details on the System information tab as follows:
System details
- Name*: A unique and relevant name to identify the system on the data map and in reports.
- Unique ID: A unique identifier for the system that is automatically generated based on the system's name.
- Description: An optional description to help other users understand what this system does.
- System tags: Optional tags you might want to associate with your system for grouping and search purposes.
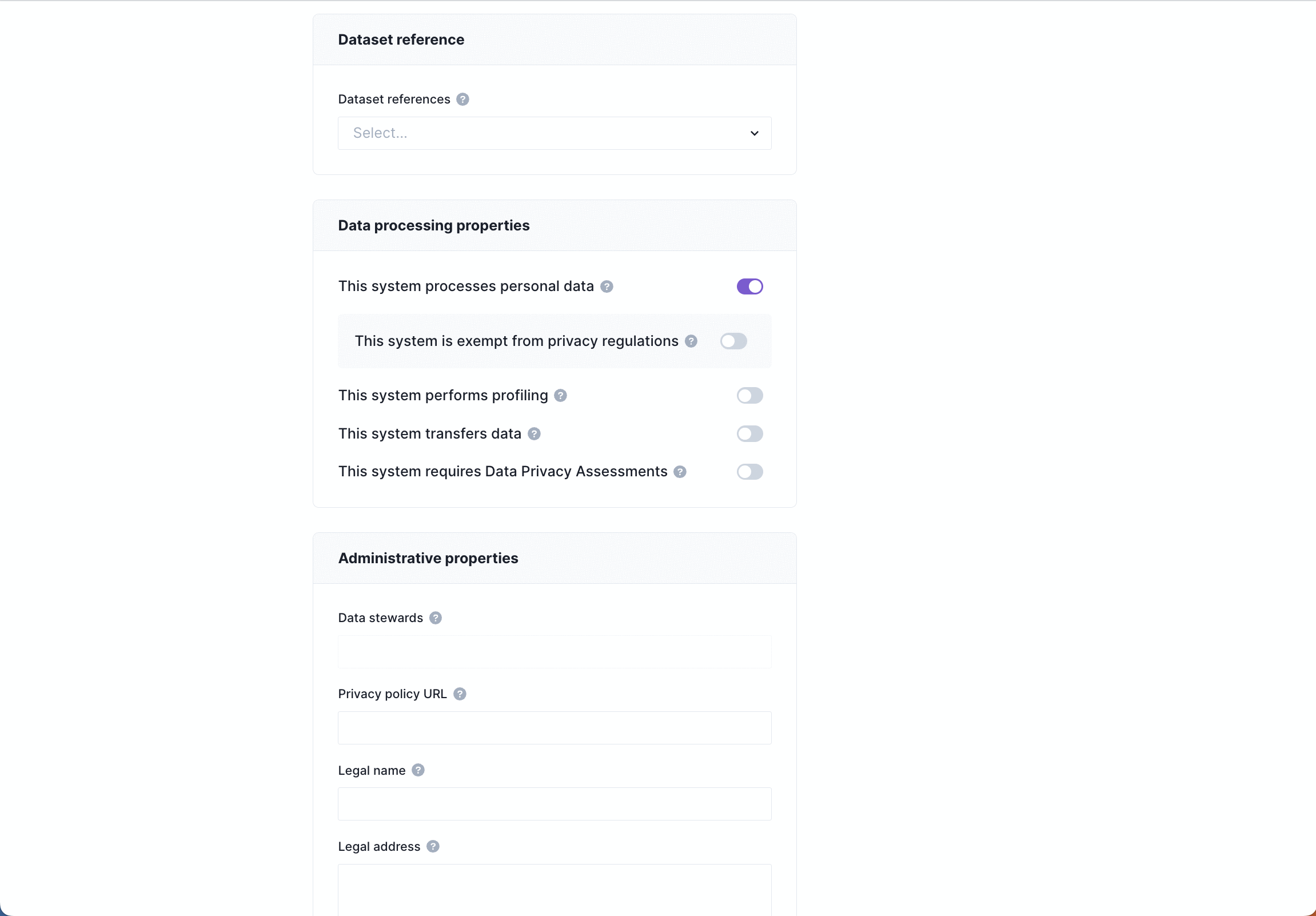
System dataset references
A dataset reference is a link to a dataset configuration that will typically describe the schema of a data store, often including annotations for data categories. When datasets are referenced by a system, the categories annotated in the dataset will appear in the data map and be available for reporting.
Cookie properties
In this section, information is stored about how this system uses cookies.
- This system uses cookies: used to indicate that the system uses cookies
- This system refreshes cookies: used to indicate that the system automatically refreshes cookies.
- This system uses non-cookie trackers: used to indicate that the system uses tracking methods other than cookies.
- Maximum duration (seconds): the maximum lifespan of a cookie, measured in seconds.
Data processing properties
In this section, declarations are made to determine which other fields will likely need to be completed for compliance purposes.
- This system processes personal data*: used to indicate that the system processes or stores personal data.
- This system is exempt from privacy regulations*: shown for systems that process personal data.
- This system performs profiling: used to indicate that the system uses automated profiling that has legal effects.
- Legal basis for profiling: the legal basis for automated profiling. Required for systems that perform profiling.
- This system transfers data: used to indicate that the system transfers data to other countries or international organizations.
- Legal basis for transfer: the legal basis for international transfer. Required for systems that transfer data internationally.
- This system requires data privacy assessments: used to indicate that the system requires a Data Protection Assessement (DPA) or a Data Protection Impact Assessement (DPIA).
- DPIA/DPA location: a link or description of where the assessment is located.
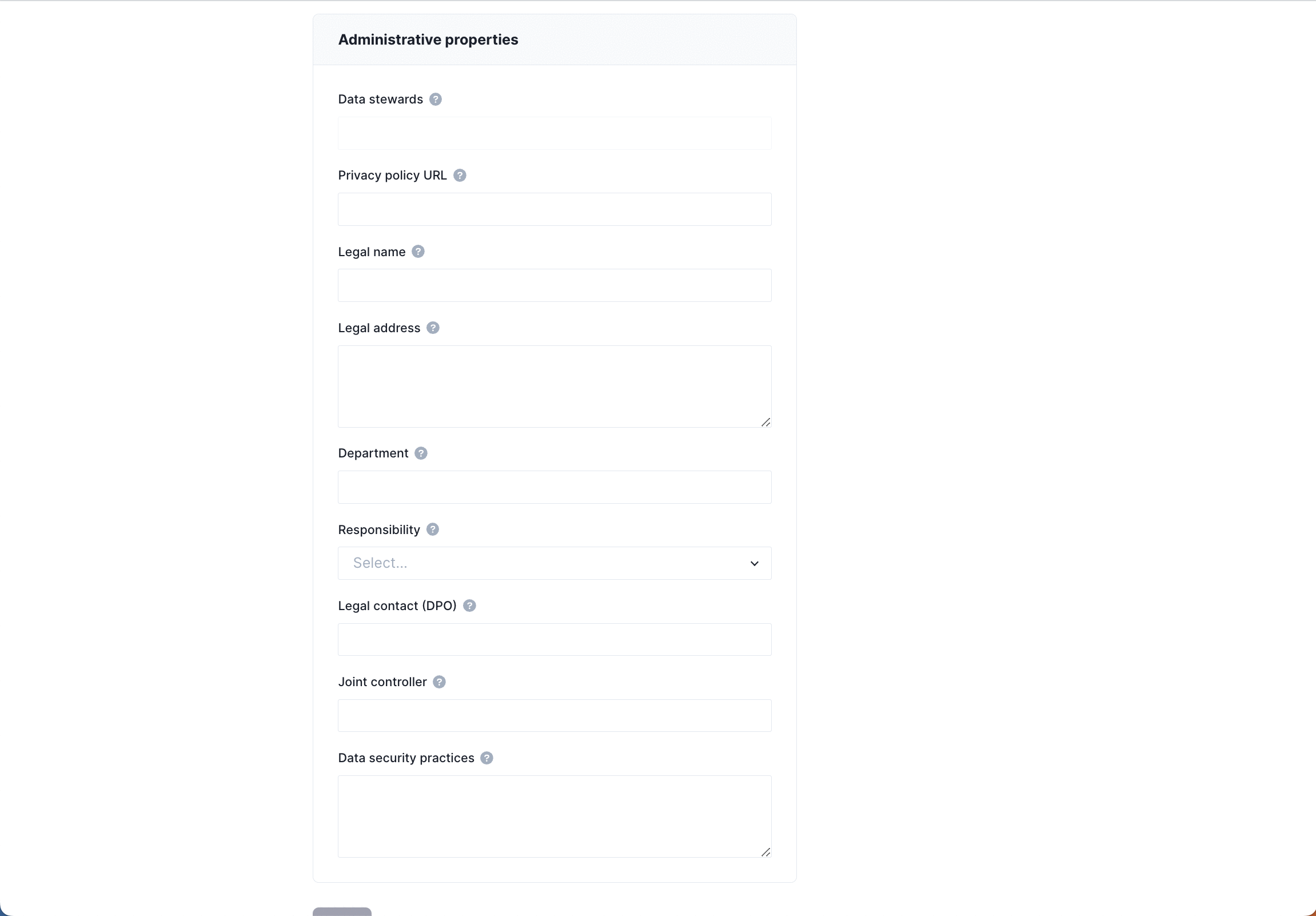
Administrative properties
- Data stewards: a list of accounts that have been assigned to the system as data stewards.
- Privacy policy URL: a link to the public-facing privacy policy that applies to this system.
- Legal name: the legal name of the business.
- Legal address: the legal address of the business.
- Department: the department that is responsible for maintaining this system.
- Responsibility: the role of the business with regard to how this system processes data.
- Legal contact (DPO): the Data Protection Officer (DPO) who is responsible for this system.
- Joint controller: the party or parties that share joint responsibility for this system.
- Data security practices: the data security practices employed to keep data in this system safe.
Next you will learn how to use automated system discovery tools. and then you will describe the ways in which you use personal data in your system.